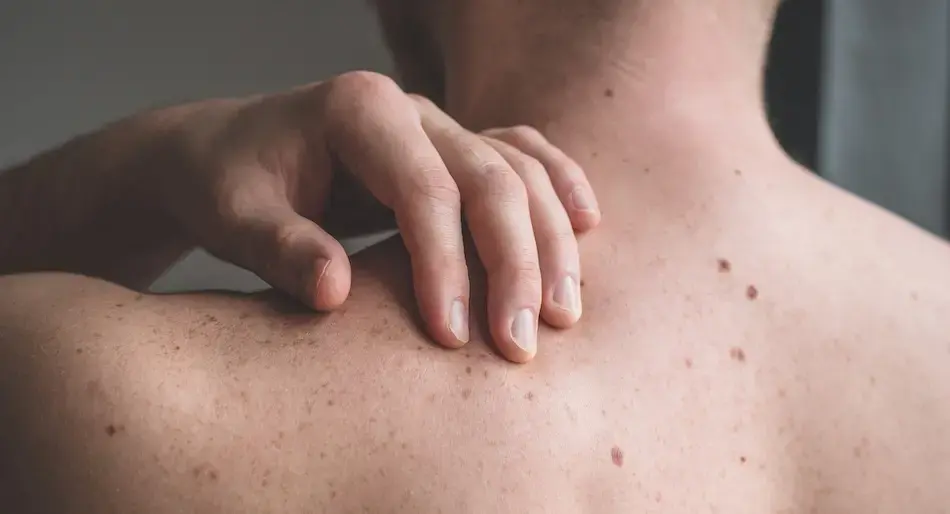
The moment of detection of a malignant skin lesion becomes transcendental to know the probabilities of accessing a timely and targeted treatment. Therefore, prevention and annual consultation with the dermatologist is key to maintain a full and vital life.
Skin cancer is divided into two types: carcinoma, which occurs in 95% of patients (not life-threatening), and melanoma (severely fatal if detected in advanced stages).
Dr. Karla Arias, specialist in Dermatology at Clínica Bíblica, emphasized that 50% of melanoma cases are diagnosed in areas of the skin free of moles. For this reason, it is important to know the profile of patients prone to develop it.
It should be noted that this cancer occurs mainly in the elderly population, with an average age of 65 years. But it also occurs in any part of the body, including the mucous membranes and eyes.
In the case of women, it is more frequently found in the extremities. In men, it is diagnosed in the head, neck and trunk.
Risk factors include:
- Heredity
- Sun exposure
- Having fair skin
- Having many moles because it makes prevention and monitoring difficult.
- Having low defenses
- Exposure to chemicals or gases
Dr. Arias explained that in her practice she usually makes a map of all the skin, "and so, by means of photographs with specialized equipment, we focus on the skin of the whole body and identify each mole: its size, shape and color. This allows us to have an order to know how many moles I have, and where they exist, in order to monitor them over time," he added.
How and when to remove a suspicious mole? "What we see in practice are patients who arrive with cancer that has already invaded other organs, and when we look at their history we find that 5 years ago they burned a mole that seemed dangerous, but it was not completely removed," Dr. Arias explained.
For that reason, it is considered key to know how to identify a malignant mole, by means of these signs:
- If it presents color changes, or redness around it.
- If it starts to itch
- If it increases in size or satellite lesions appear.
- If it has a type of ulceration or hemorrhage.
In order to make the decision to remove a mole, a series of studies are required to determine the risk, through a traditional biopsy or confocal microscopy. Thus, once the lesion has been detected, all the dangerous cells are removed, leaving a wide margin of safety beyond the mole or the affected area.
But, in addition, it must be accompanied by an interdisciplinary team, which includes a dermatologist, a pathologist, a radiologist and an oncologist.
Only in this way, and after this whole process, could the ideal drug be determined, and the start of a targeted and specific treatment.
"Advances in medicine have reduced mortality from skin cancer, but I always like to emphasize and remember that the most important thing is prevention, and annual check-ups to keep an established control," concluded Dr. Arias.
To learn more about this topic, we invite you to listen to the webinar organized by the Clínica Bíblica, in the following video: